Bộ Đề Thi Mẫu Đọc Hiểu Tiếng Anh B1 B2 VSTEP - ĐỌC HIỂU PART 2 - Đề số 1
Bộ Đề Thi Mẫu Đọc Hiểu Tiếng Anh B1 B2 VSTEP - ĐỌC HIỂU PART 2 - Đề số 1
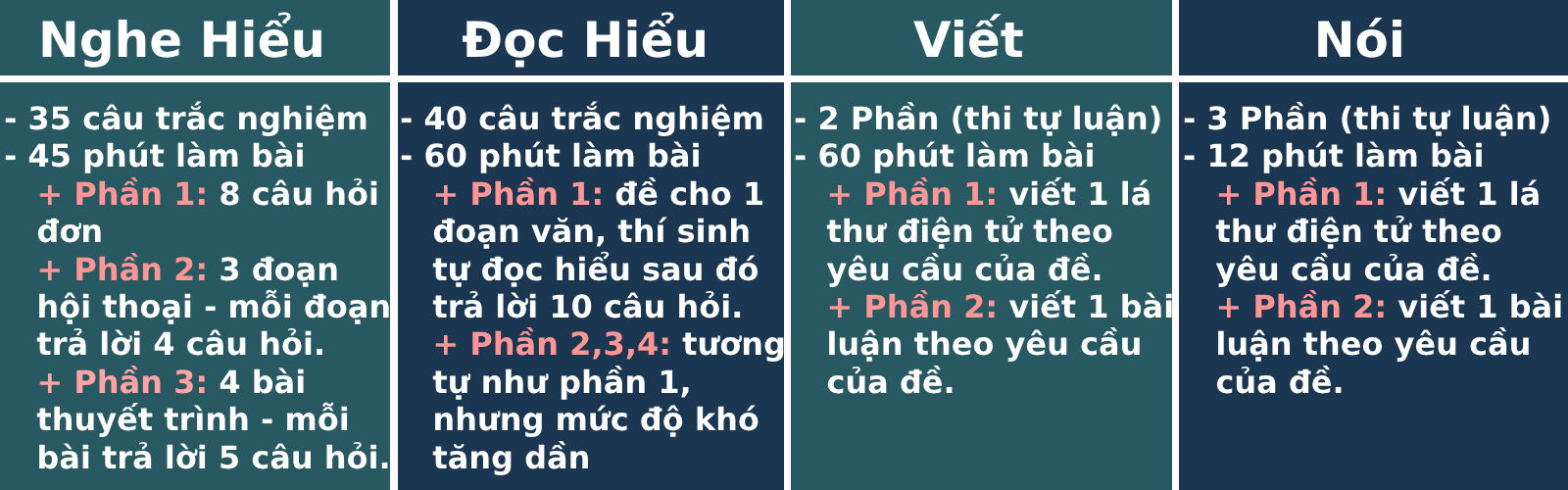
1. Cấu trúc đề thi tổng quát
2. Đề Viết B1 B2 VSTEP: ĐỌC HIỂU PART 2 - Đề số 1
Question 11-20
You should spend about 15 minutes on this task.
How does a person become an Olympic champion - someone capable of winning the gold? In reality, a combination of biological, environmental, and psychological factors, as well as training and practice, all go into making a super athlete.
[A] Perhaps the most important factor involved in becoming an elite athlete is genetics. Most Olympic competitors are equipped with certain physical characteristics that differentiate them from the average person. Take an elite athlete's muscles, for example. In most human skeletal muscles (the ones that make your body move), there are fast-twitch fibers and slow-twitch fibers. Fast twitch fibers help us move quickly. Olympic weightlifters, for example, have a large number of fast-twitch fibers in their muscles many more than the average person. These allow them to lift hundreds of kilos from the ground and over their heads in seconds. Surprisingly, a large, muscular body is not the main requirement to do well in this sport. It is more important to have a large number of fast-twitch fibers in the muscles.
The legs of an elite marathon runner, on the other hand, might contain up to 90 percent slow-twitch muscle fibers. These generate energy efficiently and enable an athlete to control fatigue and keep moving for a longer period of time. When we exercise long or hard, it's common to experience tiredness, muscle pain, and difficulty breathing. These feelings are caused when the muscles produce high amounts of lactate and can't remove it quickly enough. Athletes with many slow-twitch muscle fibers seem to be able to clear the lactate from their muscles faster as they move. Thus, the average runner might start to feel discomfort halfway into a race. A trained Olympic athlete, however, might not feel pain until much later in the competition. [B]
[C] For some Olympic competitors, size is important. Most male champion swimmers are 180 cm (six feet) or taller, allowing them to reach longer and swim faster. For both male and female gymnasts, though, a smaller size and body weight mean they can move with greater ease, and are less likely to suffer damage when landing on the floor from a height of up to 4.5 meters (15 feet)
[D] Those raised at high altitudes in countries such as Kenya, Ethiopia, and Morocco have blood that is rich in hemoglobin. Large amounts of hemoglobin carry oxygen around the body faster, enabling these athletes to run better. Cultural factors also help some athletes do well at certain sports. Tegla Loroupe, a young woman from northern Kenya, has won several marathons. She attributes some of her success to her country's altitude (she trains at about 2,400 meters, or 8,000 feet) and some to her cultural background. As a child, she had to run ten kilometers to school every day. "I'd be punished if I was late," she says.
Although genetics, environment, and even culture play a part in becoming an elite athlete, training and practice are needed to succeed. Marathon runners may be able to control fatigue and keep moving for long periods of time, but they must train to reach and maintain their goals. Weightlifters and gymnasts perfect their skills by repeating the same motions again and again until they are automatic. Greg Louganis, winner of four Olympic diving gold medals, says divers must train the same way to be successful: "You have less than three seconds from takeoff until you hit the water, so it has to be reflex. You have to repeat the dives hundreds, maybe thousands, of times." Training this way requires an athlete to be not only physically fit but psychologically healthy as well. "They have to be says Sean McCann, a sports psychologist at the Olympic Training Center in the U.S. "Otherwise, they couldn't handle the training loads we put on them. [Athletes] have to be good at setting goals, generating energy when they need it and managing anxiety."
11. What is the passage mainly about?
A. factors that make someone a super athlete
B. the different muscle types of a super athlete
C. the size of a super athlete
D. how to qualify for the Olympics
12. The word 'more' in paragraph 2 refers to
A. Olympic weightlifters
B. fast-twitch fibers
C. muscles
D. average people
13. The word 'generate' in paragraph 3 is closest in meaning to
A. waste
B. devote
C. save
D. release
14. Having a lot of slow twitch muscle fibers is particularly important for
A. cyclists
B. divers
C. weightlifters
D. runners
15. When lactate builds up in their muscles, people feel
A. strength
B energy
C. dizziness
D. pain
16. What advantage do athletes from high-altitude countries have?
A. a strong sense of culture
B. hemoglobin-rich blood
C. lower amounts of lactate in their muscles
D. more muscles in their legs
17. What is the main idea of paragraph 6?
A. Genetics is an important part of athletic success.
B. Divers must train to be successful.
C. Marathon runners must train hard to succeed.
D. Success in sports comes from a lot of practice.
18. In which space (marked A, B, C and D in the passage) will the following sentence fit? Some athletes' abilities are naturally enhanced by their environment.
A. [A]
B. [B]
C. [C]
D. [D]
19. What does Greg Louganis do?
A. a marathon runner
B. weightlifter
C. diver
D. swimmer
20. What is NOT mentioned as a factor that make an athlete successful?
A. cultural background
B. genetics
C. nationality
D. practice
3. Đáp án
11. A
12. B
13. D
14. D
15. D
16. B
17. D
18. D
19. C
20. C
