Bộ Đề Thi Mẫu Đọc Hiểu Tiếng Anh B1 B2 VSTEP - ĐỌC HIỂU PART 4 - Đề số 2
Bộ Đề Thi Mẫu Đọc Hiểu Tiếng Anh B1 B2 VSTEP - ĐỌC HIỂU PART 4 - Đề số 2
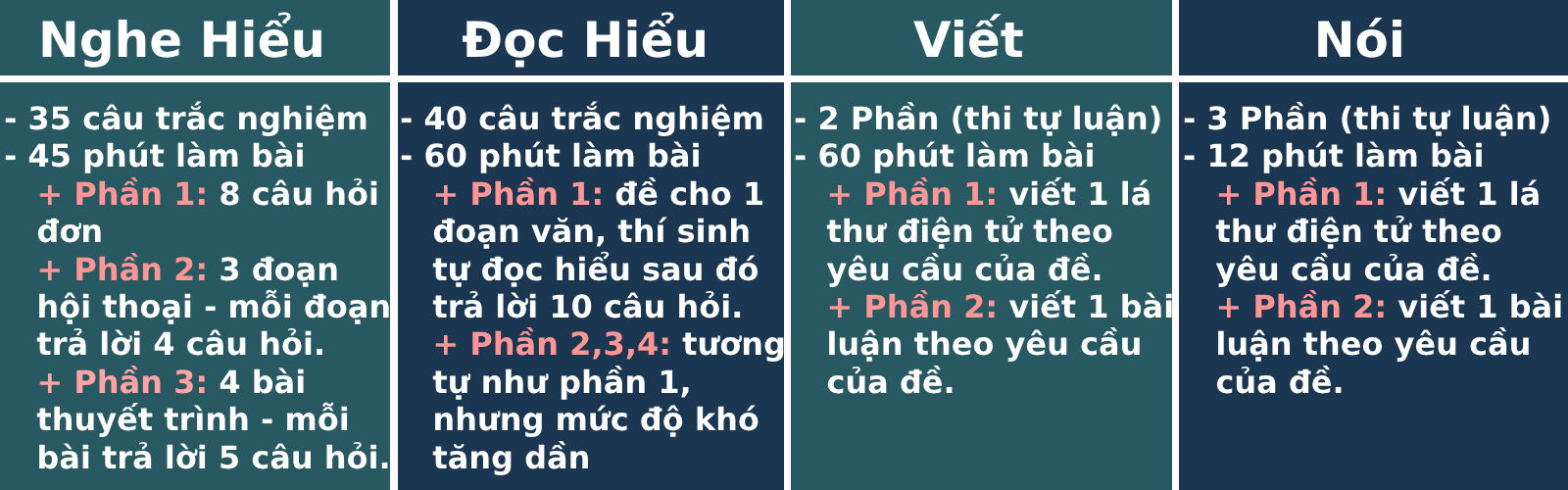
1. Cấu trúc đề thi tổng quát
2. Đề Viết B1 B2 VSTEP: ĐỌC HIỂU PART 4 - Đề số 2
Question 31-40
You should spend about 15 minutes on this task.
In recent years, the oceans have been seen as a potential source of renewable energy. Some estimates say that during the second decade of this century, ocean energy sources will generate more than 1,000 megawatts of electricity, which is enough to power a million homes in the industrialized world. Several technologies have been developed for exploiting these resources in a practical way, among which ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) is one of the most promising. Experimental OTEC plants have been constructed using different operating principles, although as yet no large-scale commercially viable plant has been launched.
The basic operation behind this system uses the heat energy stored in the oceans as a source of power. The plant exploits the difference in water temperature between the warm surface waters heated by the sun and the colder waters found at ocean depths. A minimum temperature difference of 20 degrees Celsius between surface and depth is required for efficient operation, and this situation is typically found only in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. There are two basic kinds of OTEC system: the open cycle system and the closed cycle system. In the open cycle system, the warm surface water is converted into steam in a partial vacuum and this steam drives a turbine connected to an electrical generator. In a closed cycle system, the warm surface water is used to boil a fluid, such as ammonia, which has a low boiling point. In both systems cold water pumped up from the ocean depths condenses the vapor. In the open system, the steam is condensed back into a liquid by cold water pumped from deep-ocean water and then discharged. In the closed system, the condensed ammonia is used to repeat the cycle continuously.
The OTEC system is potentially an important source of clean, renewable energy which could significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and nuclear fission. [A] Unlike other forms of renewable energy, such as those provided directly by the sun and wind, OTEC plants can generate power all the time. Furthermore, the design of this technology avoids any significant release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. OTEC can offer other important benefits apart from power production. [B] Aquaculture is one important spinoff [C] It may also be economically feasible to extract minerals from the pumped seawater. [D] Freshwater for drinking and irrigation is another by-product, and this will be an important advantage in regions where freshwater is limited.
Some drawbacks to this form of power generation have been noted. Perhaps the biggest drawback at present is the high capital cost of initial construction due mainly to the expense of the large pipeline used to pump water from 1,000 meters below the surface. Furthermore, the conversion of thermal to electrical energy in the OTEC system works at very low efficiency as the output power needed to pump a lot of water for production. There are also potential ecological drawbacks, since the water discharges will change the water temperature and disturb some marine habitats.
The main obstacle created by high initial expenses will have to be met before OTEC competes with conventional alternatives, and until such time, OTEC will remain restricted to experimental plants. When technology permits lower start-up costs, this technology will make an important contribution to world energy requirements.
31. The word 'viable' in paragraph 1 is closest in meaning to
A. clever
B. feasible
C. optimistic
D. convenient
32. It can be inferred from the passage that
A. renewable energy can be put into reservoirs
B. the experimental plants are ready to be launched
C. the oceans could be used in the future to generate electricity
D. 1,000 megawatts of electricity is the amount needed in the average home
33. How are the two basic kinds of OTEC systems similar?
A. They turn surface water into steam.
B. They use cold water to cause condensation.
C. They discharge unused water into the ocean.
D. They convert water in a vacuum.
34. The phrase 'other forms' in paragraph 3 refers to energy produced through
A. fossil fuels and nuclear fission
B. chemical reactions
C. OTEC systems
D. the sun and wind
35. What can be inferred about the different sources of energy?
A. We rely too much on fossil fuels and nuclear fission
B. Renewable energy releases a lot of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
C. Energy from OTEC is provided directly by the sun and wind.
D. Energy forms other than OTEC do not have important benefits
36. Why does the author mention aquaculture and mineral extractions in paragraph 3?
A. To give examples of possible developments related to OTEC
B. To demonstrate what other activities can be done in the ocean
C. To point out OTEC's advantages in regions of limited resources
D. To show how the environment can be improved by using clean, renewable energy
37. In which space (marked A, B, C and D in the passage) will the following sentence fit?
The nutrient-rich cold water is an excellent medium for growing phytoplankton, which provide support for various commercially exploitable fish and shellfish.
A. [A]
B. [B]
C. [C]
D. [D]
38. What is NOT a problem with the OTEC system as a power-generating system?
A. the costs of constructing the power system
B. the damage caused to fishing grounds
C. the effect of discharged water on the environment
D. the amount of water needed to produce a useful amount of electricity
39. The word 'conventional' in paragraph 5 is closest in meaning to
A. conservative
B. traditional
C. tentative
D. natural
40. Which of the following best describes the author's opinion about OTEC technology?
A. OTEC will eventually supply most of the world's energy needs.
B. The disadvantages of OTEC energy outweigh its advantages.
C. OTEC technology has a useful role to play in total energy production.
D. Only very large OTEC plants can be made efficient.
3. Đáp án
31. B
32. C
33. B
34. D
35. A
36. A
37. C
38. B
39. B
40. C
